Source Control in VS Code
Visual Studio Code allows extension authors to define Source Control Management (SCM) features through its extension API. There is a slim, yet powerful API surface which allows many different SCM systems to be integrated in VS Code, while having a common user interface with all of them.
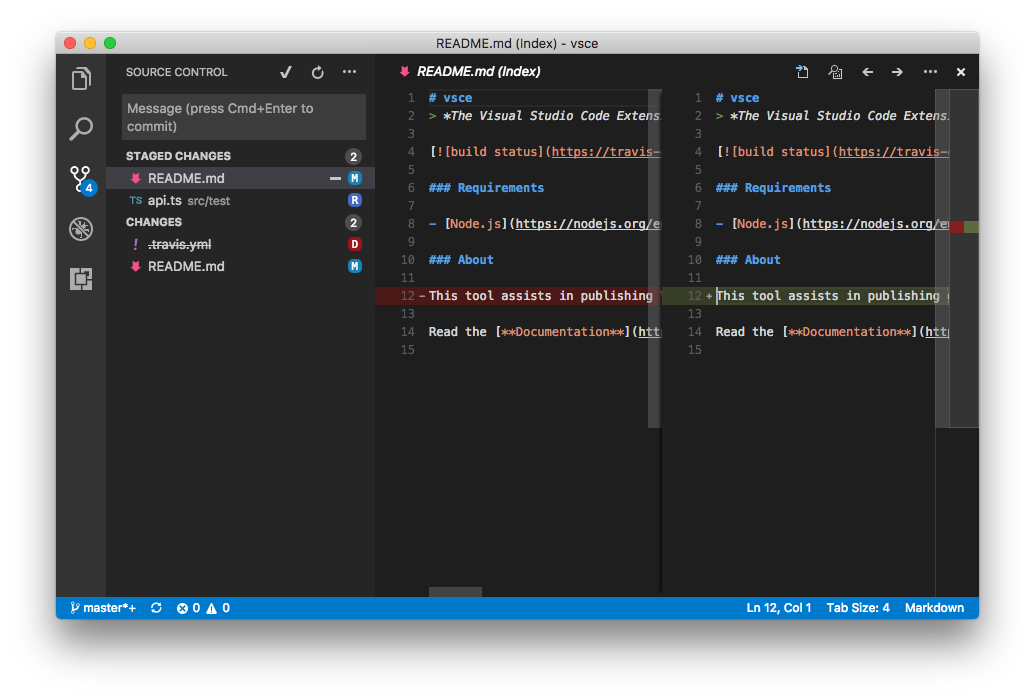
VS Code itself ships with one Source Control provider: Git. This documentation will help you integrate your own SCM system.
Note that you can always refer to the vscode namespace API reference in our documentation.
Source Control Model
An SourceControl is the entity responsible for populating the Source Control model with resource states, instances of SourceControlResourceState. Resource states are themselves organized in groups, instances of SourceControlResourceGroup.
You can create a new SourceControl with vscode.scm.createSourceControl.
In order to better understand how these three entities correlate with each other, let's take Git as an example. Consider the following output of git status:
vsce master* → git status
On branch master
Your branch is up-to-date with 'origin/master'.
Changes to be committed:
(use "git reset HEAD <file>..." to unstage)
modified: README.md
renamed: src/api.ts -> src/test/api.ts
Changes not staged for commit:
(use "git add/rm <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git checkout -- <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
deleted: .travis.yml
modified: README.md
There are many things going on in this workspace. First, the README.md file has been modified, staged and then modified once again. Second, the src/api.ts file has been moved to src/test/api.ts and that move was staged. Finally, the .travis.yml file has been deleted.
For this workspace, Git defines two resource groups: the working tree and the index. Each file change within that group is resource state:
- Index - resource group
README.md, modified - resource statesrc/test/api.ts, renamed fromsrc/api.ts- resource state- Working Tree - resource group
.travis.yml, deleted - resource stateREADME.md, modified - resource state
Note how the same file, README.md, is part of two distinct resource states.
Here's how Git creates this model:
function createResourceUri(relativePath: string): vscode.Uri {
const absolutePath = path.join(vscode.workspace.rootPath, relativePath);
return vscode.Uri.file(absolutePath);
}
const gitSCM = vscode.scm.createSourceControl('git', "Git");
const index = gitSCM.createResourceGroup('index', "Index");
index.resourceStates = [
{ resourceUri: createResourceUri('README.md') },
{ resourceUri: createResourceUri('src/test/api.ts') }
];
const workingTree = gitSCM.createResourceGroup('workingTree', "Changes");
workingTree.resourceStates = [
{ resourceUri: createResourceUri('.travis.yml') },
{ resourceUri: createResourceUri('README.md') }
];
Changes made to the source control and resource groups will be propagated to the Source Control view.
Source Control View
VS Code is able to populate the Source Control view, as the Source Control model changes. Resource states are customizable using SourceControlResourceDecorations:
export interface SourceControlResourceState {
readonly decorations?: SourceControlResourceDecorations;
}
The previous example would be sufficient to populate a simple list in the Source Control view, but there are many user interactions that the user might want to perform with each resource. For instance, what happens when the user clicks a resource state? The resource state can optionally provide a command to handle this action:
export interface SourceControlResourceState {
readonly command?: Command;
}
Menus
There are three Source Control menu ids where you can place menu items, in order to provide the user with a much richer user interface.
The scm/title menu is located to the right of the SCM view title. The menu items in the navigation group will be inline, while all the others will be within the … dropdown.
The scm/resourceGroup/context and scm/resourceState/context are similar. The former will let you customize resource groups, while the later refers to resource states. Place menu items in the inline group to have them inline. All other menu item groups will be represented in a context menu usually accessible using the mouse right-click. Commands called from within these menus will have the respective resource states on passed as arguments. Note that the SCM view supports multiple selection thus a command might receive more than one resource at a time in its arguments.
For example, Git supports staging multiple files by adding the git.stage command to the scm/resourceState/context menu and using such a method declaration:
stage(...resourceStates: SourceControlResourceState[]): Promise<void>;
When creating them, SourceControl and SourceControlResourceGroup instances require you to provide an id string. These values will be populated in the scmProvider and scmResourceGroup context keys, respectively. You can rely on these context keys in the when clauses of your menu items. Here's how Git is able to show a menu item for its git.stage command:
{
"command": "git.stage",
"when": "scmProvider == git && scmResourceGroup == merge",
"group": "inline"
}
SCM Input Box
The Source Control Input Box, located atop of each Source Control view, allows the user to input a message. You can get (and set) this message in order to perform operations. In Git, for example, this is used as the commit box, in which users type in commit messages and git commit commands pick them up.
export interface SourceControlInputBox {
value: string;
}
export interface SourceControl {
readonly inputBox: SourceControlInputBox;
}
The user can type Ctrl+Enter (or Cmd+Enter on macOS) to accept any message. You can handle this event by providing a acceptInputCommand to your SourceControl instance.
export interface SourceControl {
readonly acceptInputCommand?: Command;
}
Quick Diff
VS Code also supports displaying quick diff editor gutter decorations.
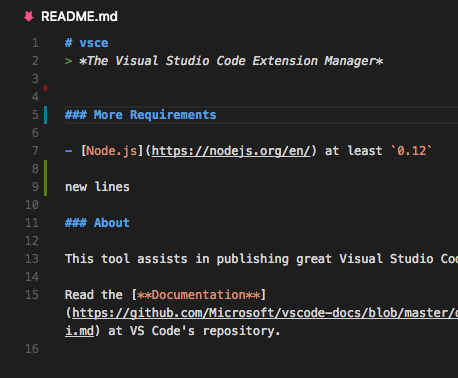
These decorations are computed by VS Code itself. All you need to do is provide VS Code with the original contents of any given file.
export interface SourceControl {
quickDiffProvider?: QuickDiffProvider;
}
Using a QuickDiffProvider, your implementation is able to tell VS Code what's the Uri of the original resource that matches the resource which Uri is provided as an argument.
You can combine this API with the registerTextDocumentContentProvider method in the workspace namespace, which lets you provide contents for arbitrary resources, given a Uri.
Next Steps
To learn more about VS Code extensibility model, try these topics:
- SCM API Reference - Read the full SCM API documentation
- Git Extension - Learn by reading the Git extension implementation
- Extension API Overview - Learn about the full VS Code extensibility model.
- Extension Manifest File - VS Code package.json extension manifest file reference
- Contribution Points - VS Code contribution points reference